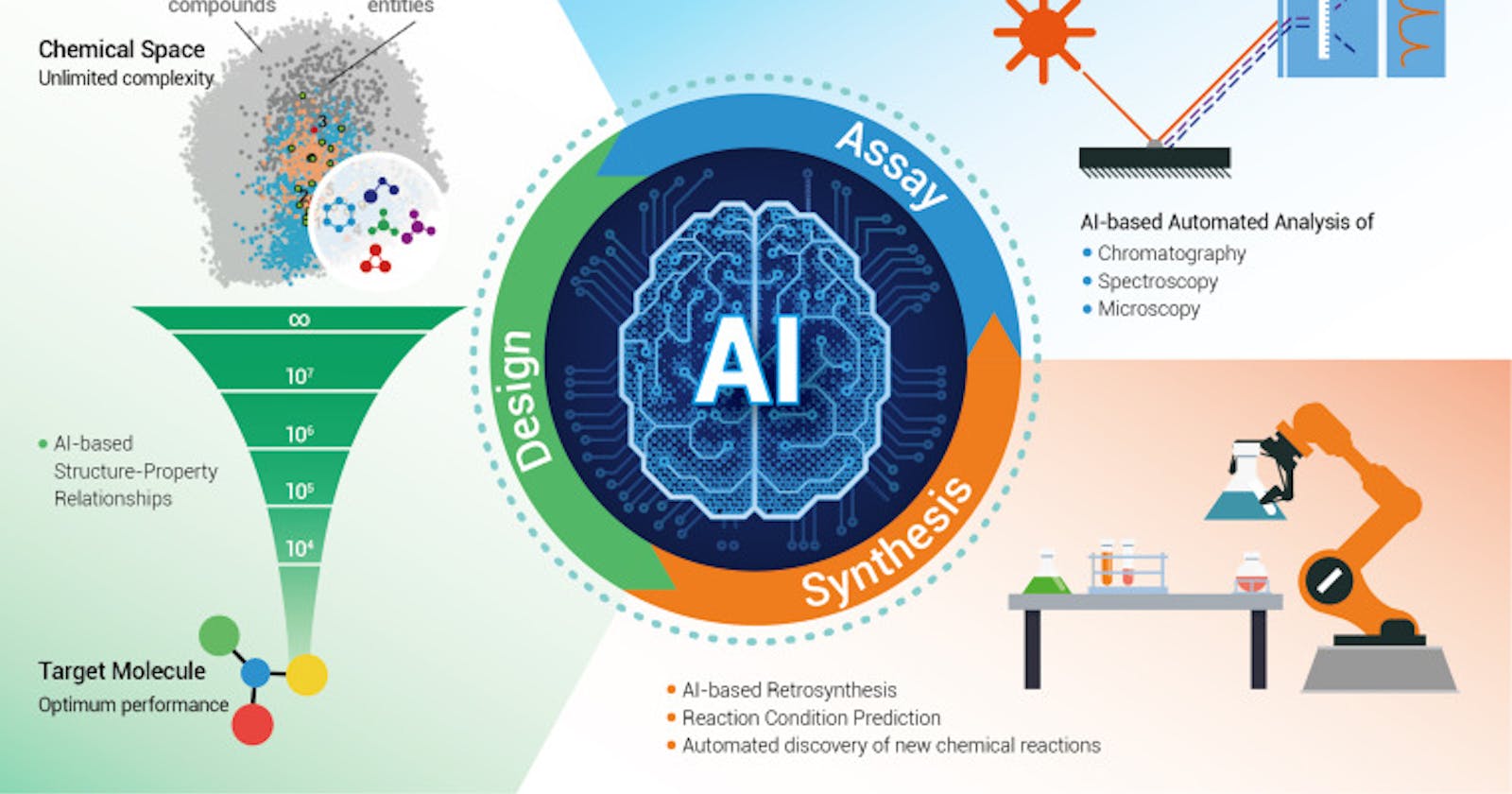
Huge information has met its match. In a large number of fields, the capacity to gather information has detonated — in science, with its expanding data sets of genomes and proteins; in cosmology, with the petabytes moving from sky reviews; in sociology, tapping a great many posts and tweets that kick back around the web. The surge of information can overpower human understanding and examination, however the registering progresses that conveyed it have additionally summoned strong new apparatuses for getting a handle on everything.
In a transformation that stretches out across a lot of science, scientists are releasing man-made reasoning (man-made intelligence), frequently as fake brain organizations, on the information downpours. In contrast to prior endeavors at computer based intelligence, such "profound learning" frameworks needn't bother with to be modified with a human master's information. All things being equal, they learn all alone, frequently from huge preparation informational collections, until they can see examples and spot abnormalities in informational indexes that are far bigger and more chaotic than people can adapt to.
Simulated intelligence isn't simply changing science; it is addressing you in your cell phone, taking to the street in driverless vehicles, and agitating futurists who concern it will prompt mass joblessness. For researchers, possibilities are generally brilliant: computer based intelligence vows to supercharge the course of revelation.
In contrast to an alumni understudy or a postdoc, notwithstanding, brain networks can't make sense of their reasoning: The calculations that lead to a result are covered up. So their ascent has produced a field some call "Computer based intelligence neuroscience": a work to open up the black box of brain organizations, building trust in the experiences that they yield.
Understanding the brain inside the machine is probably going to turn out to be more critical as simulated intelligence's job in science extends. Currently a few trailblazers are going to computer based intelligence to plan and do tests as well as decipher the outcomes, opening up the possibility of completely mechanized science. The indefatigable student may before long turn into an undeniable partner.
Artificial intelligence, in so many words
Exactly what really do individuals mean by man-made reasoning (computer based intelligence)? The term has never had clear limits. At the point when it was presented at an original 1956 studio at Dartmouth School, it was interpreted extensively as meaning causing a machine to act in manners that would be called savvy whenever found in a human. A significant late development in simulated intelligence has been AI, which appears in advances from spellcheck to self-driving vehicles and is frequently completed by PC frameworks called brain organizations. Any conversation of man-made intelligence is probably going to incorporate different terms too.
ALGORITHM A bunch of bit by bit directions. PC calculations can be straightforward (on the off chance that it's 3 p.m., send an update) or complex (distinguish walkers).
BACKPROPAGATION The manner in which numerous brain nets learn. They find the contrast between their result and the ideal result, then, at that point, change the estimations in switch request of execution.
BLACK BOX A portrayal of some profound learning frameworks. They take an info and give a result, yet the estimations that in the middle between are difficult for people to decipher.
DEEP LEARNING out How a brain network with different layers becomes delicate to additional theoretical examples dynamically. In parsing a photograph, layers could answer first to edges, then paws, then canines.
EXPERT SYSTEM A type of computer based intelligence that endeavors to imitate a human's skill in a space, like clinical finding. It joins an information base with a bunch of hand-coded decides for applying that information. AI methods are progressively supplanting hand coding.
GENERATIVE ADVERSARIAL NETWORKS A couple of together prepared brain networks that creates reasonable new information and works on through contest. One net makes new models (counterfeit Picassos, say) as different attempts to distinguish the fakes.
MACHINE LEARNING computer that track down designs in information without unequivocal guidance. A framework could figure out how to relate highlights of data sources, for example, pictures with results like marks.
Regular LANGUAGE Handling A PC's endeavor to "figure out" communicated in or composed language. It should parse jargon, syntax, and expectation, and consider variety in language use. The cycle frequently includes AI.
Brain Organization A profoundly disconnected and worked on model of the human cerebrum utilized in AI. A bunch of units gets bits of an information (pixels in a photograph, say), performs straightforward calculations on them, and gives them to the following layer of units. The last layer addresses the response.
NEUROMORPHIC CHIP A CPU intended to go about as a brain organization. It very well may be simple, computerized, or a mix.
PERCEPTRON An early sort of brain organization, created during the 1950s. It got extraordinary promotion however was then displayed to have limits, stifling interest in brain nets for a really long time.
Support LEARNING A kind of AI in which the calculation advances by acting toward a theoretical objective, for example, "procure a high computer game score" or "deal with a production line effectively." During preparing, every work is assessed in view of its commitment toward the objective.
Solid computer based intelligence computer based intelligence that is as savvy and balanced as a human. Some say it's incomprehensible. Current computer based intelligence is powerless, or restricted. It can play chess or drive yet not both, and needs sound judgment.
Directed LEARNING A kind of AI in which the calculation contrasts its results and the right results during preparing. In unaided learning, the calculation just searches for designs in a bunch of information.
TENSORFLOW An assortment of programming devices created by Google for use in profound learning. It is open source, meaning anybody can utilize or further develop it. Comparable activities incorporate Light and Theano.
Move LEARNING A strategy in AI in which a calculation figures out how to perform one errand, for example, perceiving vehicles, and expands on that information while learning an alternate yet related task, for example, perceiving felines.
TURING TEST A trial of computer based intelligence's capacity to pass as human. In Alan Turing's unique origination, an artificial intelligence would be decided by its capacity to chat through composed text.
FAQs
What is an example of artificial intelligence in research?
A menial helper like Siri is an illustration of a simulated intelligence that will get to your contacts, distinguish "Mother," and call the number. These aides use NLP, ML, measurable examination, and algorithmic execution to conclude what you are requesting and attempt to get it for you. Voice and picture search work similarly.
Why is AI important in science and technology?
Headways in simulated intelligence for applications like normal language handling (NLP) and PC vision (CV) are assisting ventures with preferring monetary administrations, medical services, and car speed up development, further develop client experience, and decrease costs.
Can AI replace researchers?
While artificial intelligence can supplant a few errands, it can't supplant human critical thinking abilities. In this manner, consolidating the qualities of artificial intelligence and human interest is important to accomplish extraordinary outcomes in logical pursuits
Original Article Published At YourQuorum